|
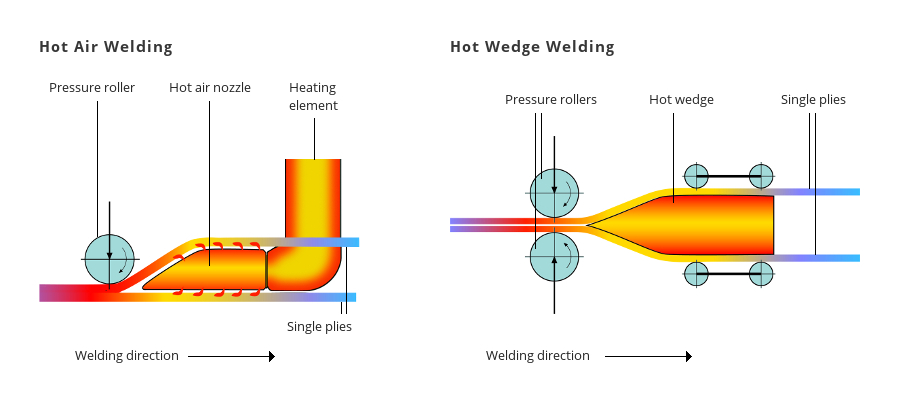
The main difference between a wedge and a hot air welder is the way in which heat is transferred to the material. With a wedge welder, a solid piece of metal—the wedge—is heated electrically and inserted between the two pieces of material. With a hot air welder, air is heated and then delivered between the two pieces of material via a hot air nozzle.
Typically, a hot wedge welder will have two sets of pressure rollers which press the heated material together to ensure a strong weld. Hot air welders typically press the material between a single pressure roller and the work surface. This makes wedge welders better suited for working on soft or moderately uneven surfaces as they weld quality is not dependent on the welding surface.
Wedge welders are generally quieter than hot air welders and are less likely to cause smoking during welding. They are also better suited for welding very thin materials as the air movement of a hot air welder can cause these materials to flutter, affecting the weld quality.
Hot air welders are generally less expensive to purchase and maintain as they do not have the ongoing cost associated with replacing wedges as they are used. Hot air welders can reach greater temperatures than wedge welders and offer control over more parameters (temperature, air flow, speed) versus wedge welders (temperature, speed). The ability to reach a higher temperature can allow for faster welding speeds as the material does not need to have as much contact with the heat source before being sufficiently heated for welding. Have questions? Contact your Technical Sales Representative for help choosing between hot air and wedge welding for your application. Comments are closed.
|
|
STANMECH Technologies Inc.
944 Zelco Drive Burlington ON L7L 4Y3 | 1-888-438-6324 | [email protected] Terms of Use Privacy Terms and Conditions of Sale Warranty Policies |
|
Proud Member of: